
Senior Content Specialist
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics covers all important derivations, formulas, and concepts of Class 12 Physics. Along with the NCERT Solutions, Important topics of the chapter, Multiple Choice Questions, Important questions and handwritten notes have also been provided that can help students with their preparation for Class 12 Exams. These notes, Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions and handwritten notes are provided in a PDF format for students to download and keep for future reference.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics – Chapter-wise Solutions
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics are provided in a downloadable PDF format in the table below.
Class 12 Physics Chapters – Important Notes
Chapter-wise important notes for Class 12 Physics are given below.
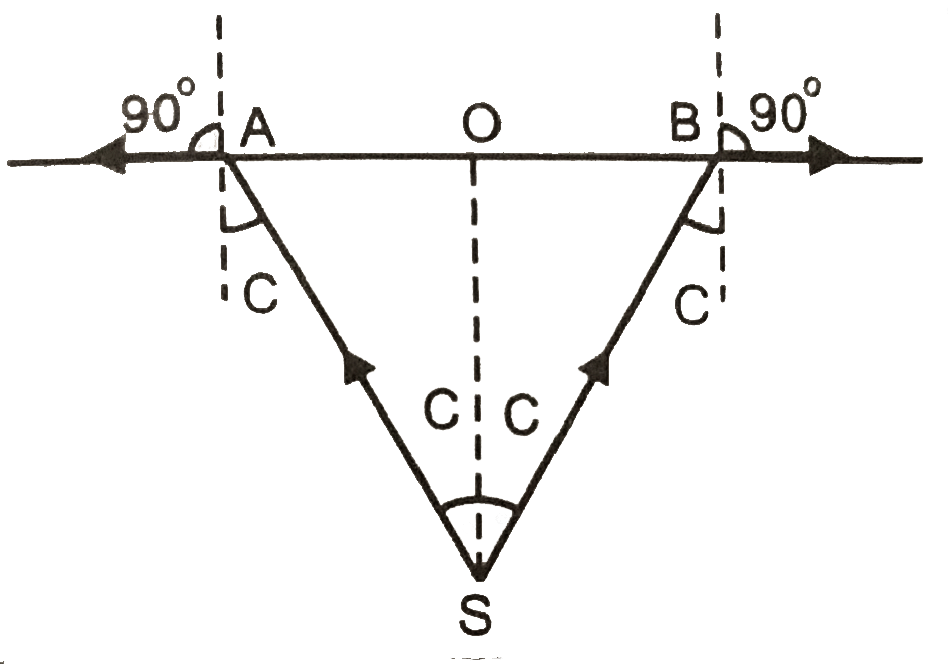
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 3 to 4 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter Electric Charges and Fields –
Additional Resources –
Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 4 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter – Along with the Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions, the important topics covered in Chapter 2 include
Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Additional Resources –
Chapter 3: Current Electricity
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 7 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 3 Additional Resources –
Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 4 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Additional Resources –
Along with NCERT Solutions of Class 12 Physics, the Moving Charges and Magnetism Handwritten Notes can also be referred by the students for preparation.
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 4 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 Additional Resources –
Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 5 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Additional Resources –
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics can be used along with Electromagnetic Induction Handwritten Notes for preparation for the board exam.
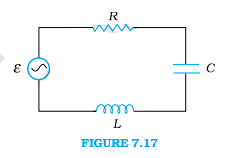
Chapter 7: Alternating Current
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 3 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Additional Resources –
Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 3 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 Additional Resources –
| Electromagnetic Waves MCQ | Electromagnetic Waves Chapter Notes | Important Questions on Electromagnetic Waves |
Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 7 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Additional Resources –
Chapter 10: Wave Optics
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 8 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Additional Resources –
Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 4 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter – The chapter notes can be used along with the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics to enhance the preparation for the board exam.
Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Additional Resources –
Chapter 12: Atoms
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 3 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Additional Resources –
Chapter 13: Nuclei
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 4 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Additional Resources –
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics
- Weightage in Board Examination – Around 7 marks
- Important Topics of the Chapter –
Class 12 Physics Chapter 14 Additional Resources –
Check Out:
Do Check Out:




Comments